Options trading offers several important benefits and reasons why traders and investors choose to incorporate them into their strategies
Most strategies used by options investors have limited risk but also limited profit potential. Options strategies are not get-rich-quick schemes and can also have unlimited loss potential.Transactions generally require less capital than equivalent stock transactions. They may return smaller figures but a potentially greater percentage of the investment than equivalent stock transactions.Even investors who use options in speculative strategies such as writing uncovered calls Select to open or close help pop-up don't usually realize dramatic returns. The potential profit is limited to the premium received for the contract. The potential loss is often unlimited. While leverage means the percentage returns can be significant, the amount of cash required is smaller than equivalent stock transactions.Although options may not be appropriate for all investors, they're among the most flexible of investment choices. Options can be used to apply a bullish, bearish or neutral strategy and utilized for generating income, hedging or speculation.
Leverage:
High Potential Returns: Options provide leverage, meaning a small price movement in the underlying asset can result in a much larger percentage gain in the option's value. You control a significant amount of stock with a relatively small capital outlay.
Capital Efficiency: Instead of tying up a large amount of capital to buy shares, you can use a smaller amount to buy options, freeing up capital for other investments.
Risk Management (Hedging):
Portfolio Protection: Options can be used as insurance to protect an existing stock portfolio from potential downturns. For example, buying put options on stocks you own can limit your losses if the stock price falls.
Defined Risk: When buying options, your maximum loss is limited to the premium paid, regardless of how much the underlying asset moves against your position. This is a significant advantage over direct stock ownership in certain scenarios.
Income Generation:
Selling Options (e.g., Covered Calls, Cash-Secured Puts): By selling options, traders can collect premiums, which can generate income, especially in sideways or slightly bullish/bearish markets. This is a popular strategy for investors looking to enhance returns on their existing stock holdings.
Flexibility and Versatility:
Profiting in Various Market Conditions: Options allow traders to profit from not just rising markets (bullish), but also falling markets (bearish), and even sideways or volatile markets.
Complex Strategie: Options enable the creation of sophisticated strategies (e.g., spreads, straddles, iron condors) that can be tailored to specific market outlooks, risk tolerances, and desired profit targets.
Customization: You can choose strike prices and expiration dates to fit your market view and time horizon.
Speculation:
Targeted Bets: Options allow traders to make highly targeted speculative bets on specific price movements or volatility changes, often with less capital risk than directly buying or shorting the underlying asset.
Event-Driven Trading: Options are frequently used to speculate on the outcome of specific events (e.g., earnings announcements, FDA approvals) that can cause significant price swings.
Diversification:
While not diversification in the traditional sense of different asset classes, options can diversify how you express your market views. Instead of just long/short stock positions, you can use options to bet on volatility, time decay, or specific price ranges.
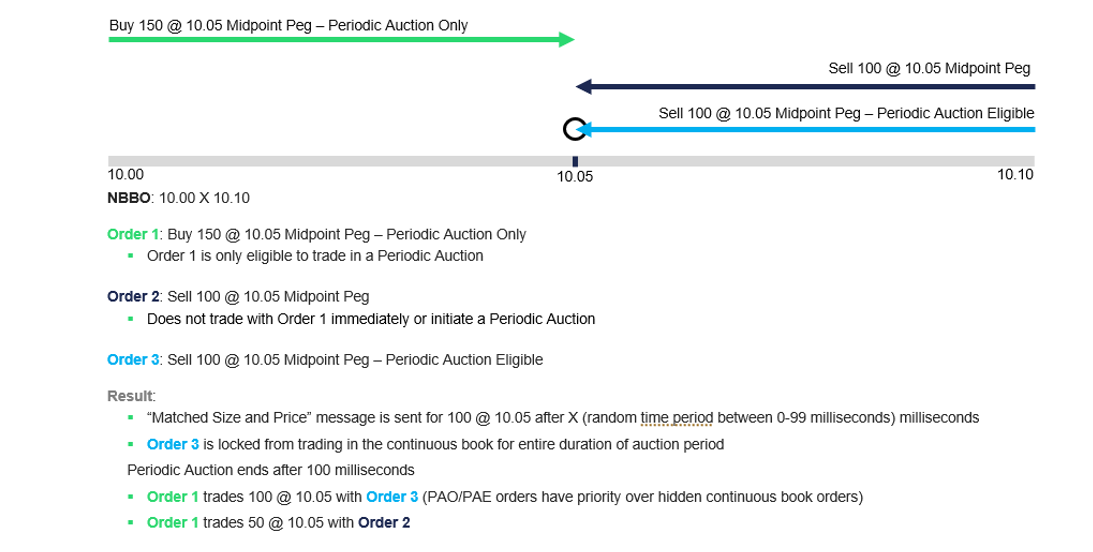
Example: PAO order and PAE order start an Auction
Potential Downsides and Why Understanding is Crucial:
Despite these benefits, it's crucial to understand that options trading also carries significant risks:
Complexity: Options strategies can be complex and require a deep understanding of how they work, including "the Greeks" (Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega), implied volatility, and time decay.
Time Decay (Theta): Options have a limited lifespan, and their value erodes over time (time decay or Theta). This works against the option buyer and for the option seller.
Liquidity: Some options contracts, especially on less popular stocks or with far-out expiration dates/strikes, may have low liquidity, making it difficult to enter or exit positions at desirable prices.
Potential for Significant Losses: While buying options limits losses to the premium paid, selling uncovered options carries unlimited risk.
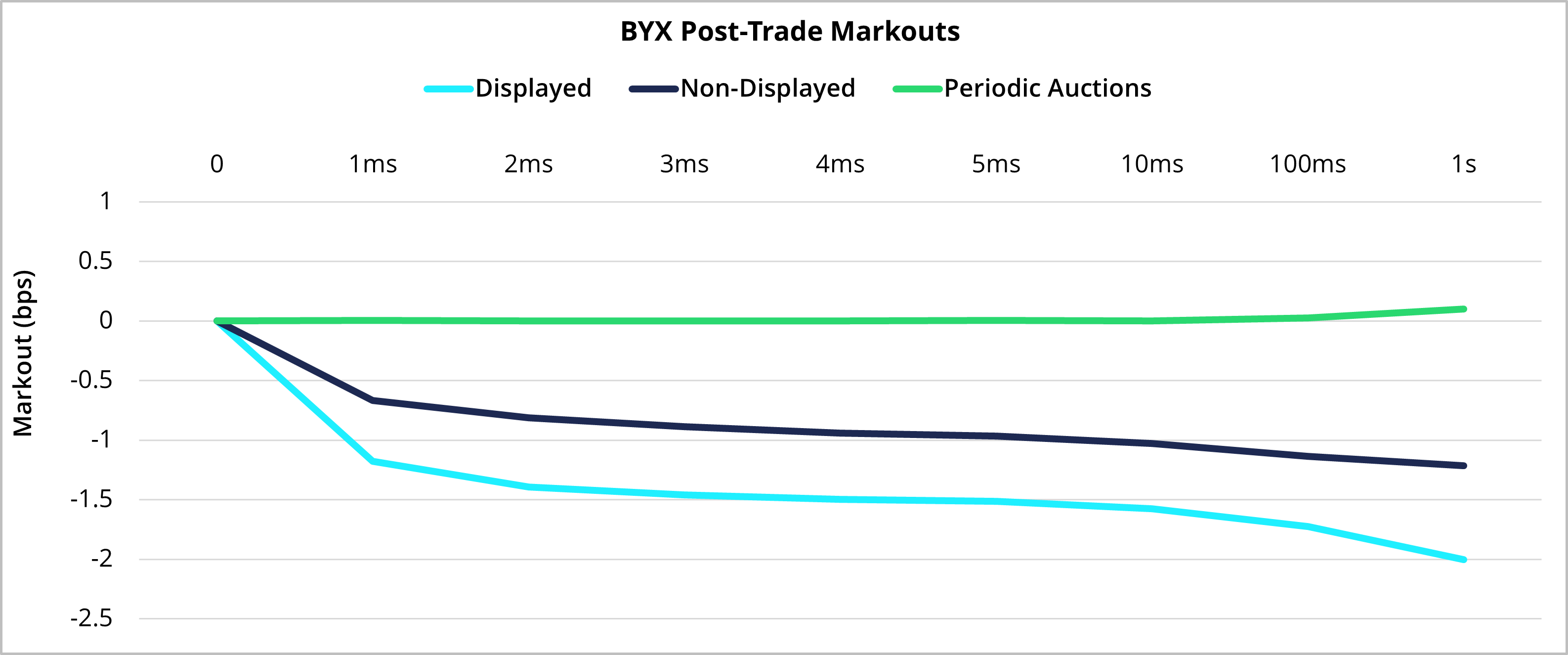
Figure 1, Source: Cboe data from December 2024 to May 2025
Periodic Auctions bring natural liquidity together and pools all available interest to trade within the spread. Pairing off like-minded participants and trading at midpoint or within the spread in an auction rather than the continuous book has resulted in greater execution quality over the period.
Options trading is important because it provides powerful tools for leverage, risk management, income generation, and versatile speculation across various market conditions. However, due to their complexity and inherent risks, they are not suitable for all investors and require a significant commitment to education and careful risk management.
There are important risks associated with transacting in any of the Share Market products discussed here. Before engaging in any transactions in those products, it is important for market participants to carefully review the disclosures and disclaimers. These products are complex and are suitable only for sophisticated market participants. In certain jurisdictions, We are only guiding to investment professionals, certified sophisticated investors, or high net worth corporations and associations. These products involve the risk of loss, which can be substantial and, depending on the type of product, can exceed the amount of money deposited in establishing the position. Market participants should put at risk only funds that they can afford to lose without affecting their lifestyle. © 2025 AIMARKETTRADE. All Rights Reserved.
